Understanding Occupational Therapy for Children
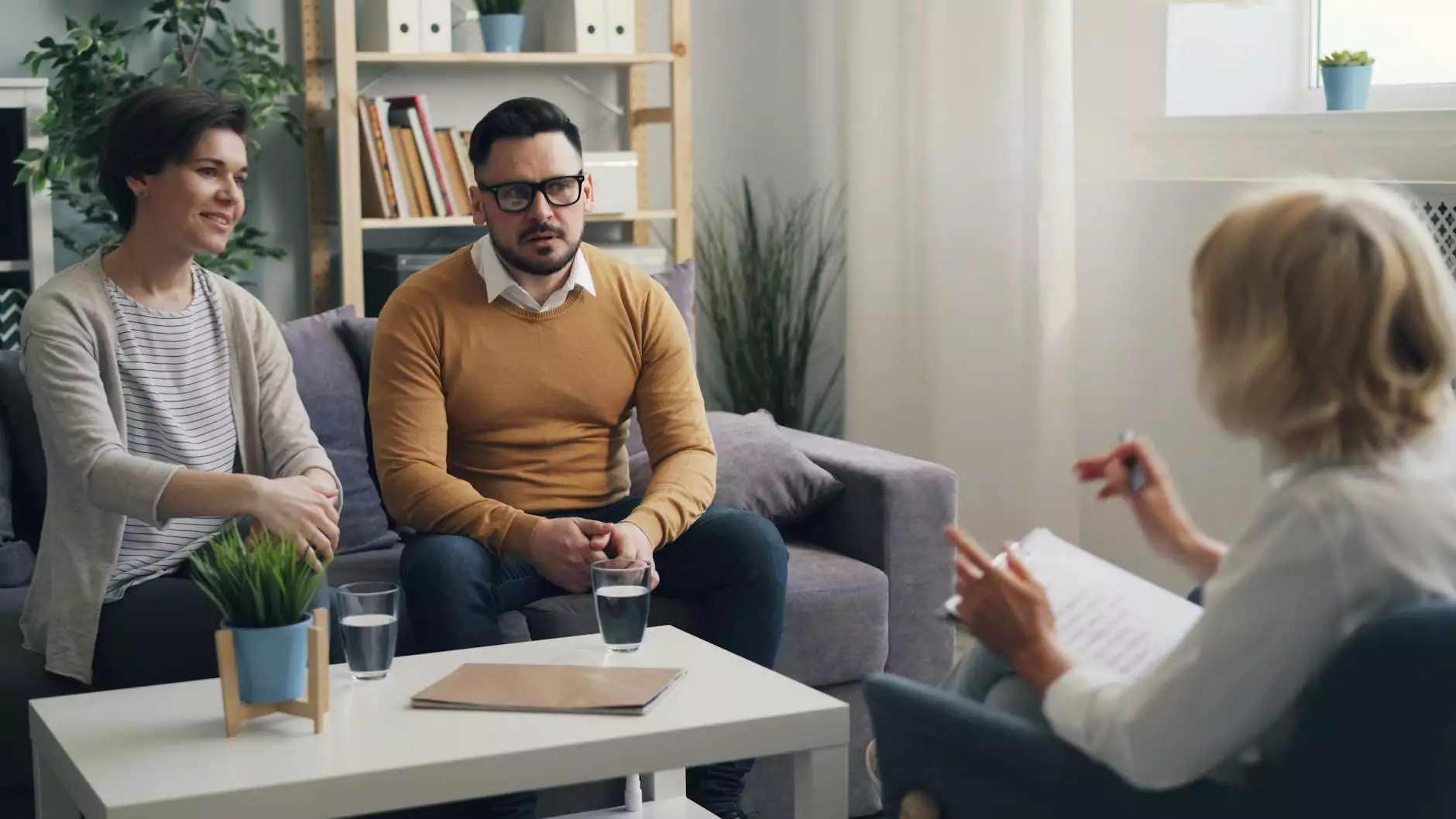

Occupational therapy for children is a specialized field that focuses on enabling children to participate in everyday activities that are essential for their growth and development. This comprehensive guide describes the importance, benefits, and processes involved in occupational therapy for children, ensuring that both parents and educators understand its vital role in child development.
What is Occupational Therapy?
Occupational therapy is a form of therapy aimed at helping individuals achieve independence in their daily lives. For children, this often involves assistance in developing the skills required for daily activities, including self-care, play, school tasks, and social interactions. It addresses both physical and developmental challenges that may hinder children from fully engaging in life’s activities.
Why is Occupational Therapy Important for Children?
The significance of occupational therapy for children lies in its holistic approach, which aims to foster not only physical abilities but also cognitive, emotional, and social skills. Here are several reasons why occupational therapy is crucial:
- Personalized Interventions: Each child is unique; hence therapy is tailored to meet individual needs.
- Promoting Independence: By developing skills, children can perform daily tasks with greater independence.
- Enhancing Social Skills: Therapy encourages interaction with peers, crucial for fostering relationships.
- Supporting Academic Success: Children gain skills essential for classroom activities, which aids in their educational journey.
- Improving Quality of Life: Through enhanced skills and confidence, children can enjoy a richer, more fulfilling life.
Who Can Benefit from Occupational Therapy?
Many children can benefit from occupational therapy, including those with:
- Developmental Delays: Delays in reaching age-appropriate developmental milestones.
- Autism Spectrum Disorders: Challenges in social skills, communication, and sensory processing.
- Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD): Difficulty focusing and completing tasks.
- Physical Disabilities: Conditions that limit physical functioning, affecting daily life.
- Emotional or Behavioral Issues: Problems that affect social interactions and school performance.
The Role of Occupational Therapists
Occupational therapists (OTs) play a vital role in providing occupational therapy for children. They assess each child’s needs and develop personalized treatment plans. Their responsibilities include:
- Evaluating Skills: Assessing the child’s abilities in various domains.
- Developing Intervention Plans: Creating targeted strategies to address specific challenges.
- Implementing Therapy Sessions: Conducting one-on-one or group therapy sessions focused on skill development.
- Engaging Families: Involving parents and caregivers in the therapy process to reinforce skills at home.
- Monitoring Progress: Continuously evaluating the effectiveness of the interventions and making necessary adjustments.
Common Techniques Used in Occupational Therapy
There are various techniques that occupational therapists utilize to help children develop the necessary skills:
- Play Therapy: Using play as a medium to help children learn and practice new skills.
- Fine Motor Skills Development: Activities such as threading beads, drawing, and cutting to enhance hand-eye coordination.
- Sensory Integration Therapy: Addressing sensory processing issues by exposing children to different sensory experiences.
- Social Skills Training: Facilitating interaction with peers through structured activities.
- Task Analysis: Breaking down complex tasks into manageable steps to aid learning.
The Process of Occupational Therapy for Children
The process of occupational therapy for children typically involves several stages:
1. Initial Assessment
The therapist conducts a comprehensive evaluation that may include interviews, observations, and standardized assessments to determine the child’s unique strengths and needs.
2. Setting Goals
Based on the assessment, the therapist collaborates with the child and parents to establish specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals.
3. Developing a Treatment Plan
A detailed intervention plan is created, outlining the techniques and activities to be employed during therapy.
4. Implementation of Therapy
Therapy is conducted through engaging sessions that incorporate play, sensory activities, and skills training to keep children motivated.
5. Progress Monitoring
The therapist regularly tracks progress toward goals, adjusting the treatment plan as necessary to ensure optimal outcomes.
Benefits of Occupational Therapy for Children
Engaging in occupational therapy for children offers numerous benefits, both in the short and long term:
- Improved Daily Living Skills: Children learn to perform self-care tasks more independently.
- Enhanced Academic Performance: Therapy addresses skills needed for school success, such as writing and attention.
- Increased Confidence: With improved skills, children often feel more confident in their abilities.
- Strengthened Family Relationships: Involving family members in the therapy process fosters collaboration and support.
- Better Social Connections: Enhanced social skills lead to improved peer interactions and friendships.
Finding the Right Occupational Therapist
Choosing the right occupational therapist is crucial for effective occupational therapy for children. Consider the following tips:
- Credentials and Experience: Verify the therapist’s qualifications and experience in working with children.
- Specialization: Select a therapist who specializes in the specific needs of your child.
- Approach and Style: Consider the therapist's methods and whether they align with your child’s personality.
- Collaboration: Look for therapists who are willing to collaborate with schools and other professionals.
- Reputation: Read reviews and seek recommendations from other parents for trusted therapists.
Conclusion
Occupational therapy for children is a critical service that can transform the lives of many children facing challenges in daily activities. By fostering essential skills, enhancing independence, and supporting emotional and social growth, occupational therapy lays the foundation for a successful and fulfilling life.
If you are interested in exploring occupational therapy for children, visit twocantalk.ca for more information and resources tailored to support your child's needs.
occupational therapy for children